Tinnitus, often described as a persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears leading to distress and discomfort, affects more than 10% of the population worldwide. For years, finding an effective treatment for this phantom auditory condition has been a challenge. One promising approach is bimodal neuromodulation.
Extensive animal studies demonstrated the ability of bimodal neuromodulation to induce neural plasticity in the auditory brain.
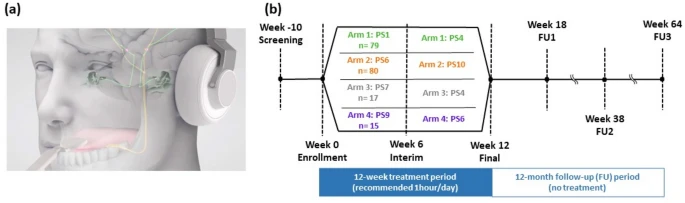
The TENT-A1 clinical trial (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT02669069) conducted in 2020 involved 326 participants and demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of bimodal neuromodulation using the Lenire device. This therapy combined sound and tongue stimulation and significantly reduced tinnitus symptom severity scores in over 80% of participants during the 12-week treatment period, with effects lasting up to 12 months after treatment. The trial used three different parameter settings (PS1, PS2, and PS3) involving synchronized sound and tongue stimulation, short interstimulus delays, and lower-frequency tones, respectively, along with background wideband noise. TENT-A2, which was statistically powered to evaluate the necessity of wideband noise, found that it was not required for therapeutic benefit in arm 2 (absent in parameter settings). Furthermore, TENT-A2 completed in 2022 (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT03530306) explored the impact of adjusting sound and tongue stimulus parameters, demonstrating significant findings in both arms (PS1-PS4 and PS6-PS10). These results represent significant progress in tinnitus treatment.
The study found that these therapeutic effects were sustained up to 12 months after the treatment ended. This long-term relief is a promising development for tinnitus sufferers.
Tinnitus treatments can be categorized into three main groups based on a recent scoping review:
Medical Technology Therapies: This category includes therapies that involve the use of medical devices or technology to manage tinnitus. Notably, the study highlighted the effectiveness of stimulation therapies, although evidence-based guidelines did not strongly recommend them. Stimulation therapies encompass approaches such as tinnitus masking, which uses external sounds to reduce the perception of tinnitus, and acoustic therapies.
Behavioral/Habituation Therapies: These therapies focus on behavioral interventions to help individuals habituate to the perception of tinnitus. Common approaches mentioned in the review include counseling, tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), relaxation techniques, and attention diversion strategies.
Pharmacological, Herbal, Complementary, and Alternative Medicine Therapies: This category encompasses treatments involving medications, herbal remedies, complementary therapies, and alternative medicine. However, the review noted a lack of significant findings and strong recommendations for these interventions, indicating the need for further research in this area.
Tinnitus research has predominantly focused on stimulation therapies and acoustic therapies. However. digital therapies, including internet-based interventions, are more cost-effective and are gaining traction in the treatment and management of tinnitus. They are showing promise in improving the effectiveness of interventions, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). They have the potential to improve patient outcomes and provide accessible options for individuals with tinnitus. However, their integration into healthcare systems requires careful consideration and the accumulation of strong evidence to support their effectiveness and long-term benefits.
REFERENCES
Conlon B, Hamilton C, Meade E, Leong SL, O Connor C, Langguth B, Vanneste S, Hall DA, Hughes S, Lim HH. Different bimodal neuromodulation settings reduce tinnitus symptoms in a large randomized trial. Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 30;12(1):10845. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13875-x. Erratum in: Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 10;13(1):11152. PMID: 35773272; PMCID: PMC9246951.
Chhaya, V., Patel, D., Shethia, F. et al. Current Therapeutic Trends for Tinnitus Cure and Control: A Scoping Review. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03910-2
No comments:
Post a Comment